Noise-canceling earphones are designed to reduce unwanted ambient sounds, offering a more immersive listening experience. There are two main types: active noise cancellation (ANC) and passive noise cancellation. While passive models rely on physical barriers like dense materials or a snug fit to block out sound, ANC technology uses advanced engineering to actively counteract noise.
Active noise cancellation works by using microphones to detect external sounds, then generating an opposite-phase sound wave to cancel the noise. This process is done in real time, making it highly effective for low-frequency noises such as airplane engine hums or traffic rumble. The result is a quieter, more focused listening environment.

The basic principle of active noise reduction involves several steps. First, a microphone captures the ambient noise. This signal is then processed by a control circuit that generates an anti-noise wave with the same amplitude but opposite phase. When this anti-noise wave combines with the original noise, they cancel each other out, resulting in a much quieter environment.
While active noise-canceling headphones offer superior performance, they come with some trade-offs. They typically require a power source, which means batteries or a charging option is necessary. In contrast, passive noise-canceling earphones don’t need any power and can still provide decent noise isolation, especially in environments with moderate background noise.
Active Noise Reduction Systems
There are three primary types of active noise reduction systems: open-loop, closed-loop, and adaptive systems. Each has its own advantages and limitations.
Open-loop System
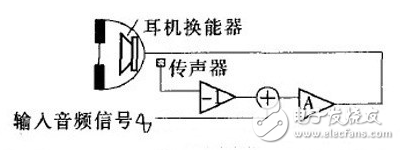
Open-loop systems use an external microphone to capture ambient noise. The signal is then inverted and played through the speaker to cancel the noise. However, because the microphone is placed outside the earcup, it may not fully capture the noise inside the ear, leading to less accurate noise cancellation. These systems are simpler and often used in consumer-grade headphones, achieving around 10–15 dB of noise reduction.
Closed-loop System
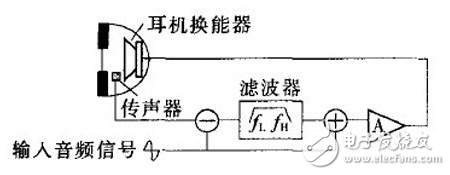
In a closed-loop system, the microphone is placed inside the earcup, capturing both the noise and the sound from the speaker. This allows the system to adjust the anti-noise signal in real time, providing more accurate noise cancellation. However, since it’s a feedback system, there's a risk of instability if not properly calibrated.
Adaptive System
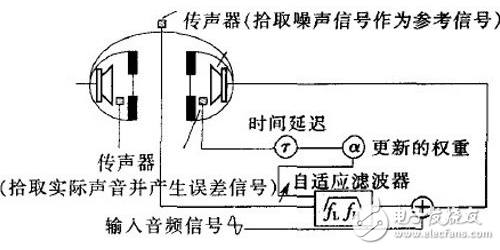
Adaptive systems use digital filters to continuously adjust the anti-noise signal based on changing environmental conditions. This makes them more flexible and efficient, especially in complex acoustic environments. By analyzing the reference noise signal and predicting how it will behave inside the earcup, these systems can deliver optimal noise cancellation without manual adjustments.
Summary
Active noise cancellation technology has evolved significantly over the years, becoming more sophisticated and widely available. Though once limited to high-end applications, it is now finding its way into mainstream consumer products. Despite its benefits, the industry still faces challenges, particularly in terms of technical secrecy and development costs.
However, the trend is moving toward greater accessibility. Several domestic brands are now developing their own ANC technologies and preparing to launch affordable options in the market. As our environments become noisier, the demand for quiet, comfortable, and intelligent audio solutions continues to grow. The future of noise-canceling headphones looks promising, with innovation driving the industry forward and bringing better experiences to everyday users.
Solar Panel,,High Efficiency Mono Solar Panels,Bifacial Jinko Solar Panels
PLIER(Suzhou) Photovoltaic Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.pliersolar.com