Abstract: According to the scientific concept of sustainable development, the article clarifies that fluorescent lamps and LED light sources are the most excellent energy-saving light sources with the latest major technical parameters. Emphasis is placed on energy consumption assessment methods and design techniques for fluorescent lamps that are truly energy efficient.
According to the statistics of authoritative departments, China's power generation reached 2.8344 trillion kWh in 2006. In 2006, China's lighting power consumption was about 340 billion kWh, which is close to 12% of the national power generation. It is almost 3.5 of China's largest Three Gorges large. The amount of electricity generated by hydroelectric power stations. Therefore, the surge in lighting power consumption and the intensification of power generation and energy consumption will make China's Power Supply situation and the status of environmental protection and ecological protection increasingly serious. If unconstrained hydropower facilities are built, it will be on the verge of destroying the natural environment. If the thermal power station is added continuously, it will further worsen the existing energy crisis. Therefore, the scientific concept of sustainable development requires, first, to strengthen the use of renewable energy, accelerate the development of various power generation technologies such as solar energy, wind energy, biomass energy, and nuclear fusion energy; second, accelerate the research on energy-saving and high-efficiency light sources and lamps, Application and development. This article mainly discusses the main points of application and development of high luminous efficiency and energy-saving light sources and lamps such as fluorescent lamps and LEDs. Focus on the energy consumption assessment method technology and design elements of fluorescent lamps that truly realize energy-saving applications.
1. The best energy-saving light source at present
   1.1 The current incandescent lamp has been quickly eliminated
   At present, in the light source of human indoor architectural lighting, incandescent lamps have been gradually eliminated due to their low luminous efficiency, excessive power consumption, and short life. For example, in the European Union, energy-saving lighting specifications for basically disabling incandescent lamps have been explicitly issued. In China, incandescent lamps have in fact withdrawn from the main areas of architectural lighting.
1.2 Under the fluorescent lamp has become the main architectural lighting source
At present, due to the advancement of novel materials, new structures, new design theories and manufacturing processes, the overall performance of fluorescent lamps has been greatly improved, for example:
1) The trichromatic phosphors with high luminous efficiency, high color rendering and high lumen maintenance have gradually replaced the traditional calcium halophosphate phosphors;
2) The optimized structural design of the new small-diameter straight tube fluorescent lamp makes the luminous efficiency of the T5 fluorescent lamp up to about 100 lumens per watt, almost ten times that of an ordinary incandescent lamp;
3) T5 thin tube straight tube fluorescent lamp, the color rendering index Ra has also reached 80 to 85 or higher, which is close to the recurrence and reduction ability of sunlight to human visible color;
4) Advanced filament and cathode design and manufacturing process, the life of T5 small diameter straight tube fluorescent lamp is generally not less than 10,000 hours, about ten times that of ordinary incandescent lamp;
5) T5 thin tube straight tube fluorescent lamp, the specification series is complete, the price has begun to be generally accepted.
The advantages of these energy-saving and high-efficiency technologies, which are constantly evolving fluorescent lamps, are the reasons why fluorescent lamps have become the main source of illumination for humans for decades. In fact, fluorescent lamps have become the most important, most common and most used source of light for architectural lighting applications worldwide. It can be said that all kinds of straight-tube or profiled fluorescent lamps, including compact integrated energy-saving lamps based on the principle of fluorescent lamps. Almost in the interior architectural lighting system, China's annual output of fluorescent lamps has reached more than 1.7 billion, and is still growing. It can be predicted that this situation will not change until the LED light source or other new light source is truly mature.
1.3 In the future, LED light source will become a newcomer to architectural lighting source
Comprehensive evaluation of LED light source is the first solid electric light source that has emerged from the human body since it understood the electric light source lighting technology. This is a revolutionary breakthrough in human lighting technology. LED light source has long life, saves energy, is easy to control light pollution, has high operational reliability, pure luminescent color, colorful light color, good controllability, small size, light weight, compact structure, simple power supply, and power supply voltage. In terms of adaptability, it is a natural spouse that can be used by renewable natural energy such as small solar power and small wind power.
At present, LED's light efficiency, thermal resistance and a series of materials and processes are making breakthroughs. The latest levels of commercial LED light sources and LED lamps in the world can be reflected:
1) The luminous efficiency of the latest commercial LED light source:
The luminous efficiency of LED products in the world is above 55lm/w to 65lm/W. The luminous efficiency of some LED light source products has been clearly marked as 100lm/W to 130lm/w, which is close to or exceeds the luminous efficiency of energy-saving lamps and fluorescent lamps. 10 times more than incandescent lamps;
2) The life of the latest commercial LED lamps:
Many international LED lighting products are marked with 70% of lumens, which are marked as 50,000 hours. Many LED lamps are marked as 100,000 hours, 10 times that of fluorescent lamps and 100 times that of incandescent lamps.
It is foreseeable that once the LED solid light source breaks through the price barrier, it will become a newcomer to the human lighting source.
2. Technical elements and energy consumption assessment methods for realizing energy-saving applications of fluorescent lamps
2.1 The key role of fluorescent lamp ballasts in energy saving of fluorescent lighting
A fluorescent lamp is a low-pressure gas discharge source, and working in the negative resistance region of the gas discharge characteristic determines that the fluorescent lamp must be equipped with a ballast to operate normally. Therefore, the overall energy-saving characteristics of fluorescent lamps are not only dependent on the fluorescent light source with excellent luminous efficiency, but the energy-saving index of the ballast is a key factor. When assessing the overall energy efficiency and energy efficiency of fluorescent lamps, it is important to evaluate the energy efficiency of the ballast.
2.2 Lighting energy efficiency indicators and grades of fluorescent lamps and ballasts
2.2.1 Lighting energy efficiency EEI of fluorescent lamp ballast and its classification
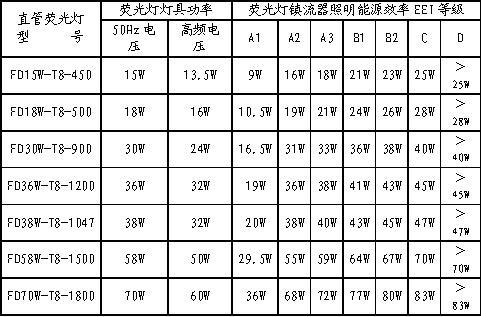
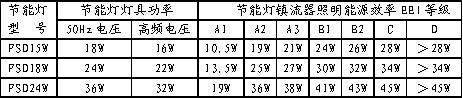
In order to truly realize the energy-saving lighting of fluorescent lamps, it is necessary to scientifically measure the energy-saving levels of various fluorescent lamp ballasts, which can be discussed here with reference to EU specifications. Internationally, especially the European Manufacture Association of Luminaries (CELMA) defines an indicator, namely Energy Efficiency In lighting, or energy efficiency EEI. In the international standard, according to the fluorescent energy ballast lighting energy efficiency EEI, the fluorescent ballast is divided into different energy efficiency levels (Classification of ballast-lamp circuit for energy efficiency in lighting) to measure different fluorescent lamp ballasts The advantages and disadvantages of power utilization efficiency and energy saving level. The lighting energy efficiency EEI of fluorescent lamp ballasts is divided into seven levels from highest to lowest: A1, A2, A3, B1, B2, C, D.
Each level defines the numerical range of the lighting energy efficiency EEI. The numerical range of the straight tube fluorescent energy efficiency EEI is shown in Table 1. The numerical range of the energy efficiency EEI of the compact energy saving lamp is shown in Table 2. At present, it is divided into two types: current value and target value. Among them: different lighting energy efficiency EEI grades, corresponding to different types and performances of fluorescent lamp ballasts, as follows:
A1 -- dimming electronic ballast;
A2 -- fixed output electronic ballast;
A3 -- fixed output electronic ballast;
B1 -- low loss inductor ballast;
B2 -- low loss magnetic ballast;
C -- traditional inductive ballast (Second phase);
D -- Early Inductive Ballast (First phase);
2.2.2 Comparison of energy saving effect and energy consumption data of fluorescent lamps with different EEI grade ballasts
Data from straight tube fluorescent lamps and compact energy-saving lamps supplied by Tridonic Atco, Tables 1 and 2, can clearly compare various fluorescent lamps and energy-saving lamps with different levels of lighting energy efficiency EEI ballast Energy saving effect and energy consumption data. Obviously, the highest level A1 of the ballast lighting energy efficiency EEI in the table should belong to the target value, and only the advanced networked digitally addressable digitally-controlled dimmable electronic ballast is used and connected to This can only be achieved in the lighting control network of infrared sensors and brightness sensors. Because all kinds of fluorescent lamps can only achieve the goal of optimizing energy-saving lighting after only networked automatic dimmable lighting.
Energy-saving effect and energy consumption data of fluorescent lamps with different lighting energy efficiency EEI grade ballasts
Energy-saving lamps with different lighting energy efficiency EEI grade ballast energy saving effect and energy consumption data table 2
2.2.3 The overall energy efficiency index LER of fluorescent lamps and the concept of “energy saving and no light savingâ€
One of the purposes of lighting technology and its lighting control technology is to focus on energy conservation, and fluorescent lamps are the most important lighting source for humans. Therefore, research and evaluation of the energy efficiency of the combination of fluorescent lamps and ballasts, that is, research and evaluation of the energy efficiency of fluorescent lamps, is extremely important for lighting energy conservation. In order to measure the overall power utilization efficiency of fluorescent lamps including fluorescent lamp ballasts, the following series of technical indicators are defined, which are physically understandable and intuitive.
1) Total luminous flux TLL (Total Lighting Lumen) (lm) of the light source inside the fluorescent lamp;
2) The total input electric power W (Watt) of the fluorescent lamp;
3) Energy efficiency of fluorescent lamps, referred to as Energy Efficiency Rating (EFF):
The luminaire energy efficiency EFF is essentially the luminaire efficiency, which is expressed by the formula 1, namely:
![]()
4) Ballast-Lamp circuit factor of ballast and fluorescent lamp circuit connection (Ballast-Lamp circuit factor), referred to as ballast lumen factor BLF: ballast lumen factor BLF is essentially a measure of ballast access The degree of influence of the energy loss on the radiant flux of the luminaire, the definition and evaluation method, expressed by the formula 2, is:
![]()
The ballast lumen factor BLF is used to evaluate how much the ballast affects the lumens of the fluorescent lamp. When the BLF is the ideal value, for example, greater than 0.95, tending to 1, the ballast is on the light of the fluorescent lamp. Radiation should not have much negative impact.
5) Define the overall energy efficiency of the fluorescent lamp as a comprehensive indicator for evaluating the overall energy efficiency of the luminaire, referred to as the Luminaire Efficacy Rating, expressed as Equation 3, as:
![]()
That is: LER = (EFF × TLL × BLF) / W (lm / w)
2.2.4 Analysis and discussion of the overall energy efficiency LER of fluorescent lamps
1) The overall energy efficiency of the fluorescent lamp LER is the luminous efficiency of the fluorescent lamp as a whole.
According to the above expression, the overall energy efficiency LER of the fluorescent lamp is dimensioned as: lm/w (lumens/watt). Therefore, from the physical concept, the overall energy efficiency LER of a fluorescent lamp can be understood as the overall luminous efficiency of a fluorescent lamp including a ballast, a fluorescent light source, and a light efficiency of a lamp. Ideally, the luminaire's efficiency EFF (luminaire light efficiency) and the fluorescent lamp ballast's lumen factor BLF tend to be 1, and both the luminaire and the ballast do not seem to lose luminous flux or energy, then, when this ideal state is reached The overall energy efficiency LER of the fluorescent lamp is equal to the luminous efficiency (TLL/W) of the fluorescent light source, but it is actually not easy to do, mainly because of the reasons described below.
2) The energy efficiency EFF (lamp efficiency) of fluorescent lamps is unlikely to be equal to 1
Due to various reasons such as materials and manufacturing processes, such as the reflectivity of the reflector of the lamp, the internal structure of the lamp and the internal scattering and luminous flux consumption of the reflector for the luminous flux, the fluorescent lamp will always have a loss of the luminous flux of the light source. The radiation of the luminous flux of the fluorescent lamp, that is, the luminous flux contributed by the fluorescent lamp to the fluorescent lamp source, is difficult to achieve 100% outward radiation. Therefore, the energy efficiency EFF of fluorescent lamps is unlikely to be close to 1.
3) The luminous efficiency of the fluorescent lamp ballast BLF and the meaning of the fluorescent lamp "energy saving and no light saving"
Fluorescent lamp ballast lumen factor BLF, on the one hand, is a measure of the extent of the power loss of a fluorescent lamp ballast. On the other hand, it can be expressed as a loss corresponding to the luminous flux (lumen) of the fluorescent lamp source. If there is a certain power loss in the fluorescent lamp ballast, the lumen coefficient BLF of the fluorescent lamp ballast cannot be close to 1, as shown in Equation 2, if BLF = 0.9, according to the expression 3 of the overall energy efficiency LER of the above lamp, Under the same conditions, the total luminous flux TLL of the light source is reduced to 0.9 times, which is a 10% discount. If the lumen coefficient BLF of the fluorescent lamp ballast reaches an ideal value close to 1, it means that the entrance of the fluorescent lamp ballast has substantially no loss to the total luminous flux TLL of the light source. Modern electronic ballasts use the following advanced technologies, such as:
Microprocessor control technology and ASIC special function ASIC;
Soft-switching (ZVS and ZCS) inverter technology with low power consumption and high efficiency;
"leisure" and "wake up" control techniques, etc.;
The luminous flux BLF of the fluorescent lamp ballast can be made close to 1, for example, greater than 0.95, etc., which not only achieves power saving, but also reduces the maximum luminous flux of the fluorescent light source, that is, the concept of "energy saving and no light saving". Obviously, while the energy efficiency EEI of the fluorescent lamp ballast reaches the highest, the BLF should also be the maximum value, tending to a better value. Therefore, the energy efficiency EEI of the fluorescent lamp ballast and its level and the fluorescent lamp ballast lumen factor BLF are extremely critical factors.
2.2.5 Selection of fluorescent lamp ballast
1) Fluorescent lighting should attach great importance to the choice of ballast
Under unfavorable conditions, even if the luminous efficiency of the fluorescent lamp is very high, but the lumen coefficient BLF of the fluorescent lamp ballast is small, the overall energy efficiency index LER of the fluorescent lamp is also inevitably low, and the same illumination is achieved for the design of the fluorescent lamp. The greater the amount of electricity that is consumed, the higher the electricity bill. Therefore, in the energy-saving design of buildings using fluorescent lighting, the selection of fluorescent lamp ballasts must be given a high degree of attention.
2) Basic basis for selection of fluorescent lamp ballasts
According to the content of “2.2 Lighting Energy Efficiency Indicators and Grades of Fluorescent Lamps and Ballastsâ€, the categories and current status of fluorescent lamp ballasts are as follows:
A1 - dimmable electronic ballast;
A2 - lower loss non-dimming electronic ballast;
A3 -- a general non-dimming electronic ballast;
B1 -- Very low loss magnetic ballast (close to China's national standard energy-saving ballast);
B2 -- low-loss magnetic ballast (approximating the ballast of China's national standard energy efficiency limit value);
C-- Traditional medium loss inductor ballast (EU was declared banned on November 21, 2005);
D-- Early high-loss magnetic ballast (EU was declared banned on May 21, 2005);
In order to minimize the reactive power loss to the grid, it is also necessary to pay attention to the power factor indicator. The above-mentioned fluorescent lamp ballast, inductive type ballast, without capacitor compensation, has a power factor of only 0.5, and after better capacitance compensation, it is preferably only about 0.80 to 0.85. Excellent electronic ballasts, especially dimmable electronic ballasts, can achieve 0.95 to 0.99. Obviously, the basic basis for the selection of fluorescent lamp ballasts is relatively clear.
3. Realizing intelligent dimming control is an important means of energy-saving lighting for fluorescent lamps
3.1 Fluorescent lamp intelligent dimming greatly saves energy and extends light source life
The dimming control of fluorescent lamps plays an extremely important role in modern lighting. Promoting the energy-saving dimming control of lighting, if aiming at the fluorescent light source that has become the mainstream in the field of lighting, is to seize the main contradiction. At present, the advanced fluorescent lamp energy-saving dimming control technology can achieve energy saving of 30%, scientifically optimized system configuration, and even achieve energy saving of 70%, which can extend the life of the light source by 2-4 times. Fluorescent lamps can only be optimized for energy saving after they have realized the computerized automatic dimming illumination.
3.2 Fluorescent lamp intelligent lithography to achieve adaptive optimization control of energy-saving lighting
Modern intelligent and networked lighting control technology can adaptively realize energy-saving dimming control according to the actual changes and needs of the lighting scene, for example: “people come to light, people are less light, people are goneâ€; “natural light Strong, the light is extinguished; the natural light is weak, the light is added; there is no natural light, the light is brightened; even in the space of the same office, the optimized energy-saving lighting adjustment and control of the partition can be realized. Another example: the lighting scene control in the building interior, not only achieves energy-saving lighting, but also meets the modern green lighting concept of humanized lighting and healthy lighting. Modern intelligent lighting control has become an important means of energy-saving lighting.
3.3 Fluorescent lamp dimming electronic ballast must meet the ballast energy efficiency index LER and ballast lumen coefficient BLF index
Fluorescent lamps are much more complicated than incandescent lamps. Fluorescent lamp energy-saving dimming control involves cross-over technology between fluorescent light source technology and electronic control technology. To do a good job of energy-saving dimming control of fluorescent lamps, we must first grasp the principle and characteristics of fluorescent lamps. Fluorescent lamps can be digitally addressed to dimming electronic ballasts. They are high-tech products of emerging lighting electronics technology. They must also be evaluated and standardized according to the ballast energy efficiency index LER described above, and the lumens of the ballasts. The coefficient BLF indicator is especially important. Currently. There are not many overall performance winners, and the application must focus on quality choices. In accordance with international or EU standards, dimmable electronic ballasts must meet the A1 rating requirements for fluorescent lamp ballast grade standards.
4. Fluorescent lamp energy-saving lighting design should comply with the "Architectural Lighting Design Standards" statutory "lighting power density value" energy-saving indicators
4.1 Architectural lighting energy-saving design should be "lighting power density value" and "illuminance" indicators double standards
Definition of "Lighting Power Density Value" (LPD): the room or location of a building, the lighting installation power per unit area (including ballast, power consumption of the transformer), in watts per square meter ( ![]() ).
).
The Architectural Lighting Design Standard (GB50034-2004) specifies the “lighting power density value†(LPD) defined by the 108 most used indoor spaces or locations in office, commercial, hotel, hospital, school and residential and industrial buildings. ).
The "Lighting Power Density Value" (LPD) specified in the Architectural Lighting Design Standard is divided into "current value" and "target value" in the same project. “Current value†refers to the current implementation; “target value†is the requirement to be achieved in the future.
The "Lighting Power Density Value" (LPD) regulations put forward higher requirements for lighting engineering design. All architectural lighting design must meet the illumination level specified in the Architectural Lighting Design Standard and the lighting power of the lighting design. The density value is limited to the “Lighting Power Density Value†(LPD) specified by the standard, thus ensuring double compliance of the lighting system and achieving effective energy saving.
4.2 Architectural lighting energy-saving design should use fluorescent lamps correctly
In architectural lighting, high-power straight tube fluorescent lamps are the most widely used. Here, high-power straight tube fluorescent lamps are taken as an example to discuss the choice of fluorescent tubes. Table 3 shows the main performance of several high-power fluorescent lamps made in China.
Performance comparison of several domestic high-power straight tube fluorescent lamps 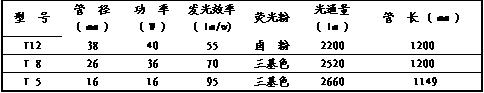
Figure 1 shows the light distribution curve of T5 fluorescent lamp. Obviously, the luminous efficiency of T5 is 30% higher than that of T8. According to Table 3, the performance of T5 high-power fluorescent lamp in domestic fluorescent lamp meets the requirements of "Architectural Lighting Design Standard" on "Lighting Power Density". The value of the (LPD) indicator is more favorable.
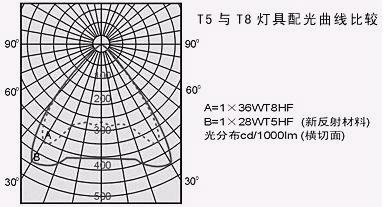
Figure 1 Comparison of the light distribution curves of T5 and T8 fluorescent lamps
5. Fluorescent lamp energy-saving lighting design should be good at using flexible lighting design methods
5.1 To fully understand the meaning of the standard to allow ±10% deviation between the design illuminance value and the standard value
In such a case, a small main control room requires a design illumination of 500 lx, encountering a realistic problem of the approved "lighting power density value" (LPD) requirements during the design process, and the current value of the power density indicator required by the national standard. For the illumination of 500lx, the current value of the illumination power density is 18 ![]() , lighting power density target value 15
, lighting power density target value 15 ![]() . Under the condition that the chamber type coefficient of the small control room, the reflectivity of the wall surface, the ceiling and the floor are constant, the average illuminance is calculated according to the utilization coefficient method, and the final selection of the fluorescent lamp luminaire is shown in Table 4.
. Under the condition that the chamber type coefficient of the small control room, the reflectivity of the wall surface, the ceiling and the floor are constant, the average illuminance is calculated according to the utilization coefficient method, and the final selection of the fluorescent lamp luminaire is shown in Table 4.
Small instrument room energy-saving lighting design case table 4 
If three T5 fluorescent tubes are used, the illuminance and illumination power density values ​​are too high and are not qualified, as shown in Table 5.
Selection of results of T5 Table 5 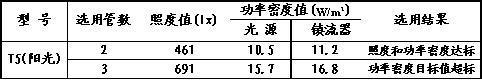
In summary, the choice of T12 and T8, illuminance and power density can not meet the standard at the same time, and T5 can be fully up to standard, when using two high-power straight tube fluorescent lamps T5, the illuminance value is 461 lx, because it is noted that "architectural The Lighting Design Standard (GB50034-2004) allows a range of ±10% deviation between the design illuminance value and the standard value, so the 461 lx still fully meets the requirements of the standard, and also allows appropriate supplementation of low-power energy-saving lamps for localization. illumination. In this case, only two T5 tubes are the best choice, and the “target value†required for the power density value is achieved, which is forward-looking. In this case, it also shows that the current technical indicators of T5 fluorescent lamps need to be further improved.
In summary, in the above case, two T5s replaced three T12 or T8 solutions, achieving energy saving priority.
5.2 Fluorescent lamp energy-saving lighting design to adjust the traditional uniform illumination mode to ignore the illumination of the secondary area
Sometimes it will be met when the lamp power density value will exceed the standard, and the lamp can reach the target. To do this, change the traditional uniform illumination mode and ignore the illumination of the secondary area, for example: small room door Areas, small areas near windows, areas where people flow, etc., focus on ensuring that the illumination on the work surface is up to standard. Here, we should reinterpret and correct the effect and significance of uniform illumination on energy-saving lighting.
5.3 fluorescent lamp energy-saving lighting design should sometimes be good at the use of medium color temperature straight tube fluorescent light source
Generally, the same type of straight tube fluorescent lamp, the light efficiency of the medium color temperature tube is better than that of the high color temperature tube. Therefore, a straight tube fluorescent lamp with a color temperature of 4000K or 4200K should be used. T5 straight tube fluorescent lamps are available in a range of products with different color temperatures. Moreover, most of the medium color temperature T5 fluorescent tubes have excellent color rendering, are warm white and have a strong seasonal adaptability.
5.4 Fluorescent lamp energy-saving lighting design should be good at adjusting the traditional uniform symmetrical lighting mode
Frequently encountered such a case, using 10 T8 illuminance can reach the standard, but the power density index exceeds the standard; and after using 7 T5 fluorescent lamps, the illuminance and illumination power density can reach the standard, at this time, the number of lamps encountered is odd. Instead of an even number, it is obviously difficult to implement the lighting according to the traditional uniform symmetrical mode. Therefore, it is necessary to change the thinking and design a lighting scheme that is both novel and beautiful, and meets the standard to ensure energy saving priority.
6. LED fluorescent light
6.1 LED fluorescent lamp challenges the dominance of fluorescent lamps
Fluorescent lamps are also commonly known as fluorescent lamps, and the main reason is that the color rendering performance of fluorescent lamps is close to daylight. Since fluorescent lamps have dominated the lighting industry for decades, they have developed extremely rich and experienced experiences in lighting applications and design, and the existing fluorescent lighting architectural lighting is extremely extensive and numerous.
In today's booming LED light source technology, LED light sources can also produce fluorescent lamps that are structurally similar to fluorescent lamps. LED luminaires will inevitably aim at fluorescent lamps, a widely used lighting luminaire, and a place where the number of existing fluorescent lamps that can be replaced and transformed can be replaced to compete for the dominant position of fluorescent lamps in the lighting industry. In fact, LED fluorescent lamps like fluorescent lamps based on LED light sources have appeared.
6.2 LED fluorescent lamp with performance and structure similar to fluorescent lamps
Figure 2 shows an LED fluorescent lamp that is similar in performance and structure to fluorescent lamps. The main technical parameters are:
1) Power consumption: 20W (maximum value);
2) Luminous flux: 1300 lm;
3) Color temperature: 3000 K – 6000 K (white, red, green, blue, orange, etc., optional);
4) Life: 100,000 hours;
5) Power supply: 230V 50/60 Hz;
6) Optical radiation angle: 120° (C0 metering plane);
7) Length: 630mm;
8) Weight: 0.70 Kg

Figure 2 is an LED fluorescent lamp with performance and structure similar to fluorescent lamps
What is the appearance of the 6.3 LED fluorescent lamp?
Obviously, it is really too early to comment on the promotion of this kind of LED fluorescent lamp, because its cost is a bit too expensive compared with fluorescent lamps! However, the appearance of such an LED fluorescent lamp indicates that the LED as a lighting source is a newcomer, and it is inevitable to enter the field of illumination occupied by the conventional fluorescent lamp in the future. Moreover, the successful manufacture of LED luminaires has proven to be superior to traditional light sources such as fluorescent lamps or compact energy-saving lamps in terms of improving the light efficiency of luminaires due to the unique "light-emitting cell" structure of LED light sources.
6.4 LED fluorescent lamp energy-saving lighting application
LED lamps in energy-saving lighting applications, similar to fluorescent lamps, will also encounter the "lighting energy efficiency indicators and grades" evaluation and specification issues, but LED Switching Power Supply technology, there is no such as high-frequency electronic ballasts A series of troubles, and the dimming control of the LED fluorescent lamp, will no longer use the dedicated electronic ballast of the fluorescent dimming control, dimming will be relatively easy. As for the LED energy-saving lighting design and other issues, you can refer to the experience of fluorescent lighting architectural lighting design, and continue to inherit and develop.
At present, LED lamps are expensive, mainly using a series of new technologies, processes and materials. With the continuous development, especially the luminous efficiency of LEDs is still rising, we can be confident that LED lamps will enter the rookie field in the field of lighting. Lighting industry.
Conclusion
In summary, the implementation of energy-saving design of architectural lighting for fluorescent lamps is also an important part of implementing the scientific concept of sustainable human development.
The energy-saving design of fluorescent lighting in buildings must focus on the following four aspects:
1) Correct selection of fluorescent light source, pay attention to the selection of high-efficiency fluorescent light source;
2) Scientific selection of fluorescent lamp ballasts, special attention should be paid to the energy efficiency EEI index and the BLF indicator of the ballast;
3) Reasonable and flexible design of fluorescent lighting energy-saving lighting for buildings, achieving double levels of “lighting power density value†(LPD) and “illuminance†indicators;
4) Promote intelligent lighting control of fluorescent lamps to optimize energy-saving lighting for fluorescent lamps;
In the foreseeable future, LED fluorescent lamps will surely enter the field of lighting, and there will be no complicated problems in application.
(End of the text)
Editor: China Lighting Network Liu Li
Laptop Adapter For Hp,Laptop Charger,Laptop Adapter For Toshiba
Laptop Adapters Wall Mount Adapter Co.,Ltd , http://www.chlaptopadapters.com