As the largest dark horse in the field of low-power WAN technology of the Internet of Things, RPMA technology has already arrived in China. As early as January this year, John Horn, CEO of RPMA technology in the United States, personally visited Wuxi and planned to base on Wuxi. The IoT infrastructure with RPMA as the core technology will be gradually expanded to the whole of China. At present, Ingenu has cooperated with Wuxi Military Intelligent Electric Co., Ltd. to establish Wuxi Jiuzhou Communication as the only authorized company of Ingenu to promote its RPMA technology and application in mainland China.
Introduction to RPMA technologyRPMA, the full name of Random Phase MulTIple Access, the official Chinese translation for "random phase multiple access", is a low-power wide area network (LPWA) technology in the Internet of Things.
What about LPWA?
LPWA, the full name of Low Power Wide Area, is a low-power wide-area network. The low-power wide-area network is a long-distance and low-power communication demand for the Internet of Things. In recent years, an Internet of Things wireless connection technology has a long transmission distance. The technical characteristics of low node power consumption, simple network structure, and low operation and maintenance cost. The emergence of low-power WAN technology has filled the gap in existing communication technologies and laid the foundation for the larger-scale development of the Internet of Things.
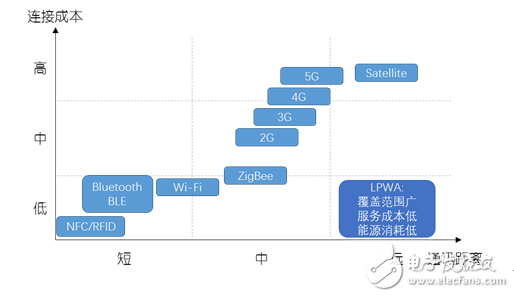
Figure 1: Coverage and connection costs of major communication technologies
For consumer Internet of Things (IoT) applications, Wi-Fi, ZigBee, and Bluetooth are ideal near-range wireless networking technologies, but for the wider range of civil, industrial, and other IoT long-haul applications, cellular networks Or satellites can meet the requirements, but these technologies are not competitive in terms of cost, power consumption, and scalability. Therefore, in the context of the development of Internet of Things technology, low-power wide area network (LPWA) technology emerged.
Low-power wide area network (LPWA) technology is very versatile, and civil infrastructure such as parking lot resources, traffic flow control, utility monitoring, power distribution control, and environmental monitoring is just the beginning, such as crop growth monitoring and livestock migration. Agricultural applications also require wide area network coverage; asset monitoring and tracking, from taxis to frozen freight, requires regional, national, and even global coverage. Transportation infrastructure such as iron and roads also requires wide-area surveillance; even consumer applications such as healthcare can benefit from WAN links that replace cellular phones.
LPWA has the characteristics of wide coverage, low service cost and low energy consumption. It can meet the connection requirements of low-speed data exchange frequency, low connection cost, convenient roaming network point switching and suitable complex environment in the IoT social environment. The ideal way of connecting things.
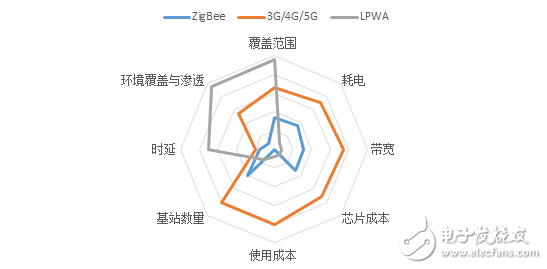
Figure 2: Comparison of the main indicators of several wide-area networking technologies
RPMA officially developed a low-power WAN access technology in the context of the development of Internet of Things technology. RPMA was developed by Ingenu, Inc., and Ingenu was established in 2008. The name of the company before September 2015 was ONRAMP. Ingenu provides developers with transceiver modules to connect to the RPMA network that the company and its partners have built around the world; these networks forward information from endpoints to the user's IT system. At the same time, RPMA can also be applied to the customer base who wants to build a private network.
Under the joint operation of the RPMA terminal and the base station, the user can manage the capacity, data rate and range of their communication; the base station keeps synchronization with the terminal node that transmits the signal within the predefined time frame, and takes a random delay from the start of the time frame, the terminal node The spread spread factor is also selected based on the received signal strength.
The access point de-spreads, deinterleaves, and Viterbi decodes the received signal after receiving the data, and then performs a CRC check. As network usage increases, the access point can command the end node to reduce their transmitted signal strength to reduce the number of nodes it must process.
Ingenu RPMA security includes two-way authentication, 256-bit encryption, and a 16-byte hash function to protect signal traffic; this solution allows the network to provide authorized software upgrades to endpoints and ensure information integrity and Resend protection.
Advantages of RPMACompared with similar products in the market, RPMA technology has obvious competitiveness. Compared with competitors' similar LPWA technology, RPMA technology has five main features:
First, the network coverage is strong. The RPMA base station has a wide network coverage, covering only 619 base stations and 1866 base stations in the entire United States and continental Europe, respectively, and 10830 base stations and 43319 base stations respectively corresponding to LoRa technology; 6840 are required for Sigfox technology respectively. Base station and 24,837 base stations. The reduction in the number of base stations has greatly reduced the construction and operation costs of the Internet of Things, so that its economic benefits are higher in the long run.
Second, the system capacity is large. Take the continental United States as an example. If the devices in the Internet of Things transmit one hundred bytes of information per hour, then RPMA technology can access 249,232 devices, while LoRa technology and Sigfox technology can only access 2,673 devices. And 9706 devices.
Third, the equipment energy consumption can be fully reduced, thereby extending the battery life as much as possible. RPMA uses power control and information transmission confirmation to reduce the number of retransmissions. The terminal enters deep sleep state at the interval of data transmission to reduce power consumption and extend battery life.
Fourth, the use of uniform frequency, easy to roam. The RPMA technology uses the 2.4G band, which is a free band all over the world, so that RPMA devices can roam around the world. Sigfox uses a frequency of 868MHz in Europe and a frequency of 915MHz in the United States, while the two frequencies 868 and 915 are already occupied in China, making it difficult to roam.
Five, two-way communication, can be broadcast. RPMA adopts the two-way communication method, which can control or upgrade the terminal device through broadcast. Sigfox uses one-way transmission, and Lora uses half-duplex communication.
RPMA technology is at a leading level in the application of Internet of Things, and will definitely promote the construction of the Internet of Things in China.
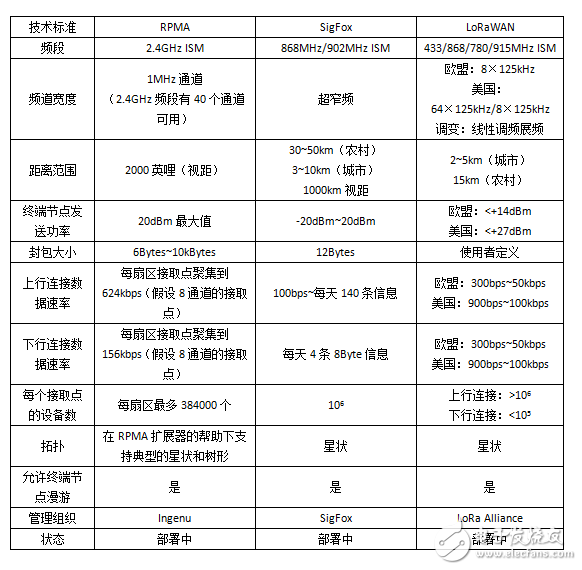
Figure 3: RPMA technical specifications compared to competitors
From the appearance, the "jumpers" of the board cards in the computer are small metal sticks (jumper posts) embedded on the motherboard, sound card, hard disk and other devices, and small clips (jumper clips) that are set on these metal sticks. The function of the jumper is to adjust the on-off relationship of different electrical signals on the device, and to adjust the working status of the device, such as determining the mainboard voltage, the master-slave relationship of the driver, and so on. When the jumper clip is put on two jumper posts at the same time, it means that the two jumper posts are connected. If only one or no jumper posts are put on, it means it is disconnected. It is very important to adjust the jumper. If it is jumped incorrectly, it may crash in some cases or even burn the entire device. Therefore, you must read the manual carefully when adjusting the jumper, and check the name of the jumper, the number of the jumper and the on-off relationship.
The jumpers on the motherboard generally include CPU setting jumpers, CMOS clear jumpers, and BIOS write prohibition jumpers. Among them, the CPU setting jumper is the most complicated. If the motherboard is relatively old, you must set the core voltage, FSB and frequency multiplier jumpers on the motherboard. According to the motherboard manual and CPU frequency, set the above corresponding jumpers. Normally, there is a set of jumpers corresponding to the CPU voltage on the motherboard, and each jumper corresponds to a voltage value. Find the appropriate voltage value, plug in a keycap to short it, and select this voltage value. In the same way, find the FSB jumper and multiplier jumper, and set the appropriate FSB and multiplier respectively. Note that only one jumper can be short-circuited in each group of jumpers.
The jumper here refers to the copper connecting wire, which is made of a standard jumper cable and connecting hardware. The jumper cable has copper cores ranging from two cores to eight cores. The connecting hardware is two 6-position or 8-position modular plugs. , Or they have one or more bare wire ends. Some jumpers have a modular plug at one end and an 8-position module slot at the other end, or are equipped with 100P wiring plugs, MICs, or module slots. Jumpers are used on the distribution frame to transfer various links, and can be used as a distribution frame or equipment connection cable. Both ends of the modular jumper are RJ45 connectors, adopt TIA/EIA-568A pin structure, and have a flexible plug-in design to prevent loosening and jamming. The length of the jumper is 1 foot (0.305 meters) to 500 feet (15.25 meters), the most commonly used are 3 feet, 5 feet, 7 feet and 10 feet. Modular jumpers are used in the work area and can also be used as jumpers in the wiring closet. In the small office network or home network DIY installation, the dual-computer interconnection jumper is often mentioned. This kind of jumper is not a standard jumper used in integrated wiring, but a special hardware device connection line. It is used when two PC computers are directly connected by twisted pair, or when two HUBs are to be connected through RJ45 ports. , You need crossover (commonly known as cross-connect wire, jumper). It follows a special connection sequence.
MTRJ Patchcord, ST Patchcord, FIN Patchcord, SC Patchcord, FC Patchcord, LC Patchcord
Shenzhen GL-COM Technology CO.,LTD. , https://www.szglcom.com